
Aqua Harmony: Harnessing Water Wisdom for a Thriving Homestead
[ ]
]
(Replace https://i.imgur.com/your_image_here.jpg with your selected image URL)
The late afternoon sun blazes down, and despite our best efforts, the tomato plants are starting to droop. The well is holding steady, but the electric bill is a stark reminder that every gallon pulled from the ground comes at a cost – both financially and environmentally. Sound familiar? We've all been there, watching the weather forecast with bated breath, hoping for a downpour that never seems to come. But what if you could take control of your homestead's water destiny, reducing your reliance on municipal sources and building a more resilient, self-sufficient ecosystem?
The good news is, you can! Beyond the standard garden hose and sprinkler, there's a world of creative water management techniques just waiting to be explored. This post will unlock the secrets to rainwater harvesting, greywater recycling, and efficient irrigation, empowering you to cultivate a thriving, water-wise homestead that can weather any dry spell. We'll dive into specific strategies, offering practical tips and insights that can transform your approach to water conservation. So, grab a glass of something cool, and let's embark on this journey toward a more sustainable and abundant future for your home and garden!
Rainwater Harvesting: Catching the Sky's Gift
[ ]
]
(Replace https://i.imgur.com/your_image_here.jpg with your selected image URL)
Rainwater harvesting is often the first thing that comes to mind when discussing water conservation, and for good reason. It's a relatively simple way to collect a valuable resource that would otherwise run off into storm drains. But let's move beyond the basic rain barrel and explore some more advanced techniques for maximizing rainwater capture on your homestead.
Beyond the Barrel: While a standard rain barrel is a great starting point, consider investing in a larger cistern for increased storage capacity. These can be above-ground or buried underground, offering various advantages in terms of space and temperature control. Cisterns are typically made of plastic, metal, or concrete. Plastic cisterns are lightweight and relatively inexpensive, but they may degrade over time from UV exposure. Metal cisterns are durable and can be painted to match your home's aesthetic, but they can be prone to rust. Concrete cisterns are incredibly strong and long-lasting, but they are also the heaviest and most expensive option.
Don’t forget about gutter modifications! Installing gutter guards prevents debris from clogging your downspouts, ensuring a consistent flow of water into your collection system. A first-flush diverter is also crucial. This simple device redirects the initial rainwater runoff, which is often contaminated with dirt, leaves, and other pollutants, preventing it from entering your cistern.
Calculating Your Needs: Before investing in any rainwater harvesting equipment, it's essential to calculate your water needs. Consider the size of your garden, the climate you live in, and your average water usage. For example, a 100-square-foot vegetable garden in a dry climate will require significantly more water than a small herb garden in a rainy region. There are many online calculators that can help you estimate your water needs based on your specific circumstances.
Filtration and Purification: Rainwater is generally clean, but it's important to filter it before using it for irrigation or other purposes. A simple sediment filter can remove larger particles, while a UV sterilizer can kill bacteria and other microorganisms. For irrigation, basic filtration is often sufficient. However, if you're considering using rainwater for potable purposes (drinking, cooking), you'll need a more comprehensive filtration system and should consult with a water quality specialist. It is vital to emphasize here that you should never use collected rainwater for potable purposes without the necessary filtration and purification steps. Always check your local regulations before drinking harvested rainwater.
Legal Landscape: Rainwater harvesting regulations vary widely from state to state and even from municipality to municipality. Some areas encourage rainwater harvesting with incentives and rebates, while others have restrictions or even outright bans. Before setting up a rainwater harvesting system, it's essential to research your local regulations and obtain any necessary permits. A good starting point is your local water authority or environmental protection agency.
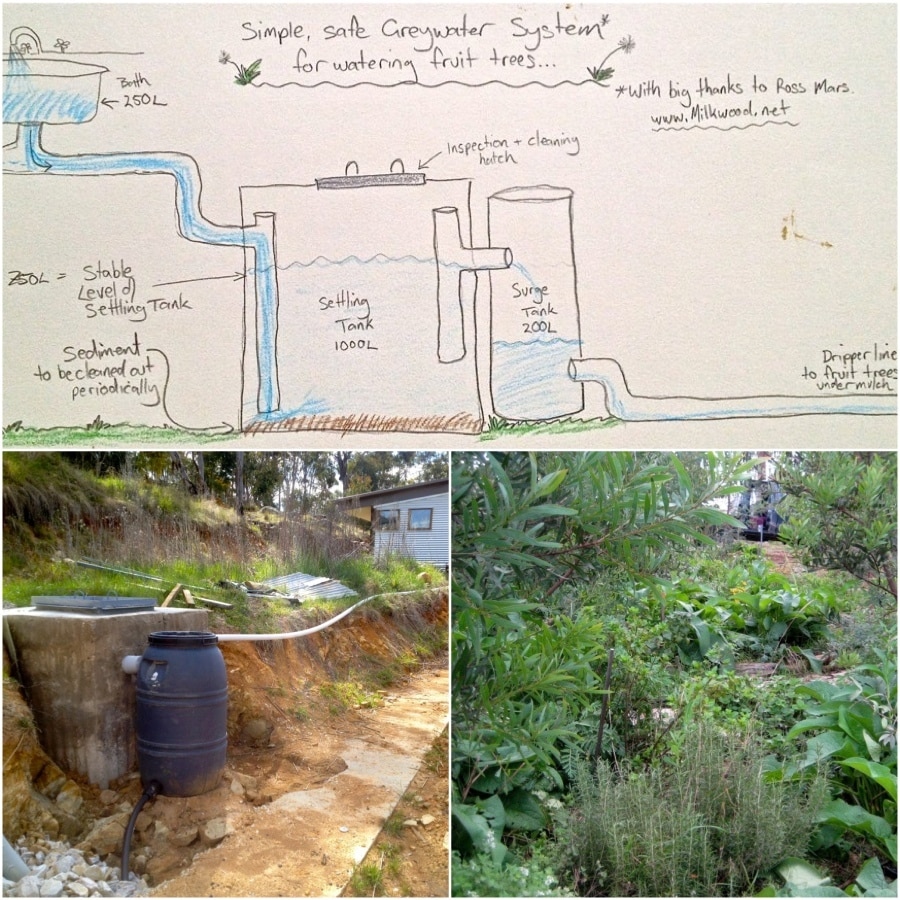
Greywater Recycling: The Second Life of Household Water
[ ]
]
(Replace https://i.imgur.com/your_image_here.jpg with your selected image URL)
Greywater recycling offers another innovative way to conserve water on the homestead. Instead of sending water from your showers, sinks, and washing machine down the drain, you can reuse it to irrigate your garden.
What is Greywater (and What Isn't): Greywater is defined as wastewater from showers, sinks, and washing machines. It does not include water from toilets, kitchen sinks (due to food contamination), or dishwashers. Using greywater significantly reduces your freshwater demand, conserving a precious resource. However, it's crucial to handle greywater safely to prevent potential health and environmental risks.
Simple vs. Complex Systems: The complexity of your greywater system will depend on your budget, skill level, and local regulations. A simple "bucket and mulch basin" system can be used to collect laundry water. This involves diverting the washing machine's drain hose into a bucket and manually transferring the water to a mulch basin around your plants. For more complex systems, you can install a plumbing system that diverts greywater from your showers and sinks to a storage tank and then to your garden.
Plant Compatibility: Not all plants are suitable for greywater irrigation. Edible plants where the water comes into direct contact with the harvest (e.g., leafy greens, tomatoes) should be avoided, as they can pose a health risk. Plants like ornamentals, trees, and shrubs are generally more tolerant of greywater. Check with your local extension office for a list of plants that are safe to irrigate with greywater in your region.
Soap Selection: The type of soap and detergent you use is critical when recycling greywater. Avoid products containing harsh chemicals, phosphates, or boron, as these can harm plants and soil. Opt for biodegradable, phosphate-free soaps and detergents specifically designed for greywater systems.
Legal Requirements & Building Permits: Greywater regulations are often very strict, so it's crucial to check with your local authorities before installing a system. Many areas require permits and inspections to ensure that greywater systems are installed and operated safely. Be prepared to provide detailed plans and documentation to demonstrate compliance with local regulations.
Smart Irrigation: Watering Wisely for Maximum Impact
[ ]
]
(Replace https://i.imgur.com/your_image_here.jpg with your selected image URL)
Even with rainwater harvesting and greywater recycling, it's essential to use water efficiently in your garden. Smart irrigation techniques can help you maximize water usage and minimize waste.
Beyond the Sprinkler: While sprinklers can be convenient, they often waste water through evaporation and runoff. Explore alternative irrigation methods that deliver water directly to plant roots, where it's needed most.
Drip Irrigation Demystified: Drip irrigation systems consist of a network of tubes and emitters that slowly release water directly to the soil. This minimizes evaporation, reduces weed growth, and prevents the spread of foliar diseases. Drip irrigation systems can be customized to suit any garden size and plant spacing.
Soaker Hoses & Wicking Beds: Soaker hoses are another efficient way to deliver water to plant roots. They are made of porous material that slowly releases water along the length of the hose. Wicking beds are raised garden beds with a waterproof liner and a layer of gravel at the bottom. Water is added to the gravel layer and then drawn up into the soil through capillary action, providing a constant source of moisture to plant roots.
Mulching Magic: Mulching is a simple but effective way to reduce evaporation and retain soil moisture. Organic mulches, such as straw, wood chips, and shredded leaves, also improve soil health as they decompose. Inorganic mulches, such as gravel and plastic sheeting, can also be used, but they don't offer the same soil-enhancing benefits. Aim for a mulch layer of 2-4 inches thick.
Smart Controllers & Moisture Sensors: Smart irrigation controllers automatically adjust watering schedules based on weather conditions and soil moisture levels. These controllers use data from weather stations and soil moisture sensors to determine when and how much water is needed, preventing overwatering and underwatering. They can be programmed to water at specific times of day, based on plant needs, and can even be controlled remotely using a smartphone app.
Upcycling Water Wisdom: Creative Repurposing for Water Conservation
[ ]
]
(Replace https://i.imgur.com/your_image_here.jpg with your selected image URL)
Water conservation doesn't have to be expensive. With a little creativity, you can repurpose everyday items to save water and add a touch of farmhouse charm to your homestead.
Upcycled Pond Liners: Old tarps, shower curtains, or even flexible pond liners can be repurposed as pond liners for small water gardens or even larger ponds. This prevents water from seeping into the ground and allows you to create a beautiful and functional water feature.
Repurposed Water Containers: Old plastic bottles, containers, or buckets can be transformed into self-watering planters. Simply drill a few small holes in the bottom of the container, add a layer of gravel, and then fill with soil. The gravel will act as a reservoir, providing water to the plant roots as needed.
Creative Water Features: Encourage readers to upcycle materials to create simple water features like bird baths or small fountains that recycle water. Include DIY instructions for a simple solar fountain, perhaps using a recycled plastic tub as the base, a small solar panel, and a submersible pump.
Reviving Antique Water Pumps: Show how old-fashioned hand-operated water pumps can be restored for a charming, functional homestead feature. These can be used to pump water from a well or cistern, adding a touch of nostalgia to your garden.
Embracing the Flow: A Sustainable Water Future
[ ]
]
(Replace https://i.imgur.com/your_image_here.jpg with your selected image URL)
Water conservation is more than just a trend; it's a necessity for creating a sustainable and resilient homestead. By embracing these water-wise techniques, you can reduce your reliance on municipal sources, lower your water bill, and cultivate a thriving garden that can withstand even the driest conditions. Remember, every drop counts, and even small changes can make a big difference. As the leaves begin to turn and the air grows cooler, consider these water management techniques as essential investments for next year's garden.
What are your favorite water-saving tips? Share them in the comments below, and let's work together to build a more water-wise future for our homes and harvests!